
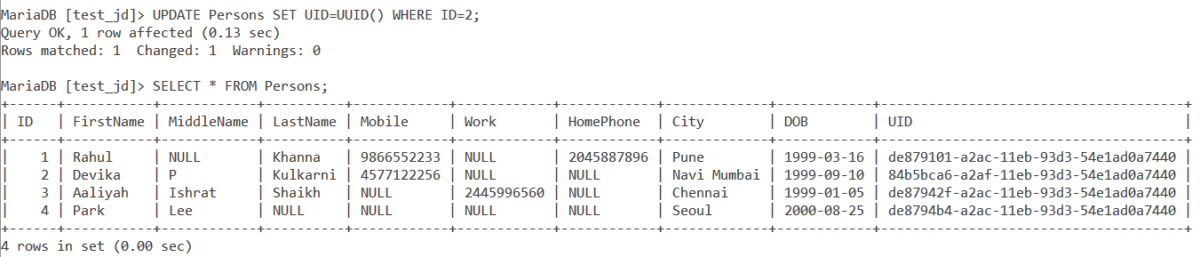
4th group is 4 characters = 2 bytes, starting with a: 8, 9, A, or B SET = CONCAT(HEX( FLOOR(ASCII(RANDOM_BYTES( 1)) / 64) + 8), SUBSTR(HEX(RANDOM_BYTES( 2)), 2, 3)) 3rd group is 4 characters = 2 bytes, starting with a: 4 SET = CONCAT( '4', SUBSTR(HEX(RANDOM_BYTES( 2)), 2, 3)) 2nd group is 4 characters = 2 bytes SET = HEX(RANDOM_BYTES( 2)) Here's the function, with comments explaining each group: CREATE FUNCTION uuid_v4() RETURNS CHAR( 36)īEGIN - 1st group is 8 characters = 4 bytes SET = HEX(RANDOM_BYTES( 4)) Universally unique identifiers (UUIDs) are 128-bit (16-byte) numbers that are designed to be globally unique, and as a result they make for great primary keys.
#Generate uuid mysql how to
In this tutorial, you have learned about MySQL UUID and how to use it for the primary key column.Why You Should Use UUIDs for Your Primary Keys To query data from a UUID column, you use BIN_TO_UUID() function to convert binary format to human-readable format: SELECT VALUES(UUID_TO_BIN( UUID()), 'John Doe'), To insert UUID values into the id column, you use UUID() and UUID_TO_BIN() functions as follows: INSERT INTO customers( id, name) The following statement creates a new table named customers: CREATE TABLE customers ( Let’s take a look at an example of using UUID as the primary key. The following are the valid string-format UUID in MySQL: aaaaaaaa-bbbb-cccc-dddd-eeeeeeeeeeeeĬode language: SQL (Structured Query Language) ( sql ) MySQL UUID example In case the argument is NULL, the IS_UUID() function returns NULL. If the argument is not valid string format UUID, the IS_UUID function returns 0. The IS_UUID() function returns 1 if the argument is a valid string-format UUID. The UUID_TO_BIN() function converts a UUID from a human-readable format ( VARCHAR) into a compact format (BINARY) format for storing and the BIN_TO_UUID() function converts UUID from the compact format ( BINARY)to human-readable format ( VARCHAR) for displaying. Notice that UUID_TO_BIN(), BIN_TO_UUID(), and IS_UUID() functions are only available in MySQL 8.0 or later. In MySQL, you can store UUID values in a compact format ( BINARY) and display them in human-readable format ( VARCHAR) with help of the following functions:

To generate UUID values, you use the UUID() function as follows: UUID() In MySQL, a UUID value is a 128-bit number represented as a utf8 string of five hexadecimal numbers in the following format: aaaaaaaa-bbbb-cccc-dddd-eeeeeeeeeeeeĬode language: SQL (Structured Query Language) ( sql ) Two UUID values are expected to be distinct, even they are generated on two independent servers. UUID is designed as a number that is unique globally in space and time.
UUID is defined based on RFC 4122, “a Universally Unique Identifier (UUID) URN Namespace). UUID stands for Universally Unique IDentifier. Summary: this tutorial introduces you to MySQL UUID, shows you to use it as the primary key (PK) for a table, and discusses the pros and cons of using it as the primary key.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
